What is blended learning?
Blended learning is a term that is popping up everywhere in education today. The UvA also defines the term blended learning in its 2022 vision. But what exactly is blended learning?
Definition
Barend Last uses the view of Torrisi-Steele (2011) in his book Blended learning in de praktijk: Modellen, strategieën, voorbeelden en andere handvatten (2022). Here, blended learning is described as follows:
The student is at the centre of the educational design. As a lecturer, you think about how the student learns best to achieve the learning outcomes.
The learning activities or teaching techniques you choose as a lecturer fit well together. In doing so, the student is motivated to actively participate in their own learning process.
As a lecturer, you aim for as much interaction as possible in your lesson design, both synchronous (students are expected to be present at the same time to learn) and asynchronous (students choose where and when to learn) and both offline and online. The transfer is between you as a lecturer and the students, between students and the content, and among students themselves. IT can be used to support different learning activities.
As a lecturer, you initiate activities – both inside and outside contact hours – to increase interaction. This concerns the interaction between you as a lecturer and the students, between the students and the content, and among the students themselves. You supplement traditional lectures and tutorials with an activating (online) environment in which students can go deeper into the material, work together on assignments, exchange ideas on discussion forums, give feedback to each other and test themselves.
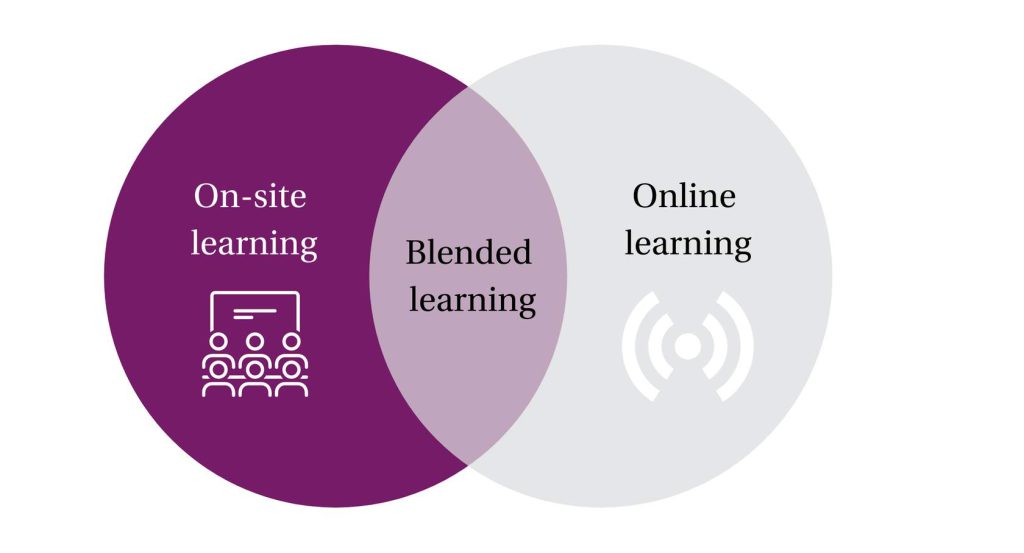
Blended learning combines the strengths of face-to-face teaching with the advantages of online teaching to enrich students’ learning. The direct contact between lecturer and student is complemented by the presence of the educational material at any place, at any time. In doing so, the online environment complements the offline environment.
Synchronous vs. asynchronous learning
Blended learning can include both synchronous and asynchronous learning. In synchronous learning, all students learn at the same time, but may be in different places (e.g. some students in the classroom and some students online). This is often the case with lectures. In asynchronous education, students control the time and place of their learning, so they do not all learn at the same time. This is often the case with (homework) assignments.
Active learning
An important theoretical foundation for blended learning is that it contributes to active learning. Active learning is, among other things, about (the variety of) teaching methods offered to students that require students to actively contribute to the learning process and encourage them to think critically. By involving students actively in the learning process right from the start, for example through active teaching methods and (formative or summative) interim tests, students are prevented from actively focusing on the material only at the end of the course, when they have to take exams.
Blended learning encourages students to actively learn in between contact moments. There are many ways to do this. There is no one default method fits every course. Learning objectives and learning outcomes guide the choice of learning activities (and assessment). Examples of online blended learning activities are:
- Activating prior knowledge, e.g. through a quiz
- Collaborative assignments
- Discussions
- Offering knowledge clips/podcasts/blogs/vlogs
- Creating a virtual reality environment
- Formative tests
- Using (peer) feedback tools
As a lecturer, you use the input from these online activities as input for the face-to-face contact moments.
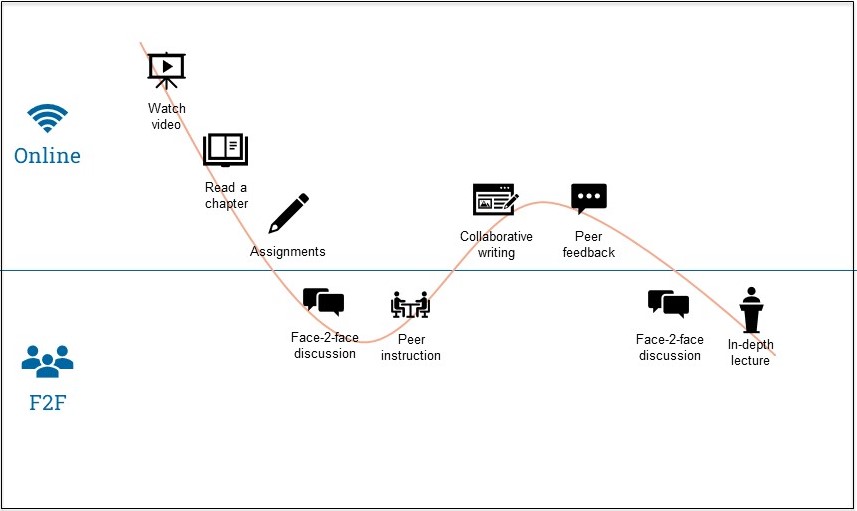
Blended learning wave
To design your ideal blend, you can use the blended learning wave (Dijkstra, 2022). This is a visualisation of the student’s learning journey during your course. It shows the sequence of all the activities your students have to go through and shows whether the activities take place online or in class.
If you want to make your own wave, you can use these sheets from Dijkstra (see also Dijkstra’s website for all workshop materials). These materials can be freely reused, as long as you refer to the original material.

Example of a blended learning wave
For more information on implementing blended learning in your teaching, read How to implement blended learning in my programme?.
Frequently Asked Questions
No, it is not the same thing. Blended learning refers to educational activities that are a systematic and meaningful combination of face-to-face interactions (offline) with online interactions between students, lecturers and educational resources. Blended learning is used as a means to improve the quality of education from a strong educational perspective.
No, it is not the same thing. Blended learning usually implies a combination of online and face-to-face activities and instructional strategies, while online learning (also called e-learning) does not involve face-to-face contact.
No, it is not the same thing. Blended learning has both synchronous and asynchronous aspects. For example, students complete homework assignments in an online environment prior to class, in their own time (asynchronous). Then, the students and the lecturer meet simultaneously in class to discuss the assignments, for discussion, questions and in-depth learning (synchronous). Hybrid teaching is a synchronous form of teaching: One group of students is physically present in the classroom, while the other group of students simultaneously participates online.
Active learning is about (the variation in) teaching methods offered to students that require students to actively contribute to the learning process and encourage them to think critically. By involving students actively in the learning process right from the start, for example through activating teaching methods and formative assessment, students are prevented from actively focusing on the material only at the end of the course, when they have to take the exam.
For an overview of active learning techniques, see also:
- UvA TLC – Ebook on interactive teaching techniques (ENG)
- UvA TLC – Activerende werkvormen voor hoorcolleges en werkgroepen (NL)
- UvA team ICTO FGW – Handreiking werkvormen activerend leren en blended learning (NL)
- HvA – Interactive tool to find the right active teaching techniques (Activitool) (NL)
- UMC Utrecht – Activerende werkvormen (NL)
- Griffith University – Active learning design tool (ENG)
Yes you can. You don’t need a high-tech classroom to get started with blended learning. Blended learning goes hand in hand with active teaching techniques, and there are countless offline options to accomplish this.
In large introductory classes, blended learning activities and active teaching techniques can support students. For example, students can participate in online exercises, online quizzes and other activities that allow for more frequent feedback. In this way, you can create small-scale learning in large groups of students.
In lectures with smaller groups (and often at higher levels), the interaction between blended learning and active teaching techniques can actually be strongly expressed. Online interactions between students (and between students and lecturer) are enhanced by face-to-face interactions online and in the classroom.
You can start by using active teaching techniques during lectures such as discussions and short writing assignments or online by using tools, such as Peerceptive or an online asynchronous discussion forum. More examples can be found in the tool selector.
Developing knowledge clips or producing web lectures takes a bit more time, but these forms of blended learning offer more time for interaction with the student during contact hours. Many forms of blended learning are possible, so who knows, you may already be “blending” yourself!
Also read How to implement blended learning in my programme? to learn more about starting with blended learning.
No. The more expertise you have, the more opportunities you can imagine. But you can get all the support you want, in terms of content, technical and didactic. Contact us for your options.
Yes. TLC Central offers a BKO+ training where you will learn how to design a blended course and get to work on your own course design. The TLC Science offers a similar pre-BKO training and professional consults for customized advice, for example if you have specific questions about implementing blended learning in your course. And blended learning is also a standard component of the BKO training.
Support and questions
Would you like to discuss a blended learning educational design or do you have other questions on this topic? If so, please contact the Teaching & Learning Centre for advice.
Sources
Dijkstra, W.P. (2022, 25 mei). De blended learning wave. Blending your education. Geraadpleegd op 16 maart 2023, van https://blendingyoureducation.nl/de-blended-learning-wave/
Last, B. & Jongen, S. (2021). Blended learning en onderwijsontwerp. Van theorie naar praktijk. Boom.
Last, B. (2022). Blended learning in de praktijk. Modellen, strategieën, voorbeelden en andere handvatten. Boom.
Torrisi-Steele, G. (2011). This thing called blended learning – a definition and planning approach. Research and Development in Higher Education: Reshaping Higher Education.