It is recommended that teachers appeal to a variety of the students’ thinking skills with their courses. Within a curriculum, assessment as a whole should also address plain understanding as well as higher-level thinking skills. Bloom’s taxonomy may be of help in distinguishing between thinking skills and formulating assignments accordingly.
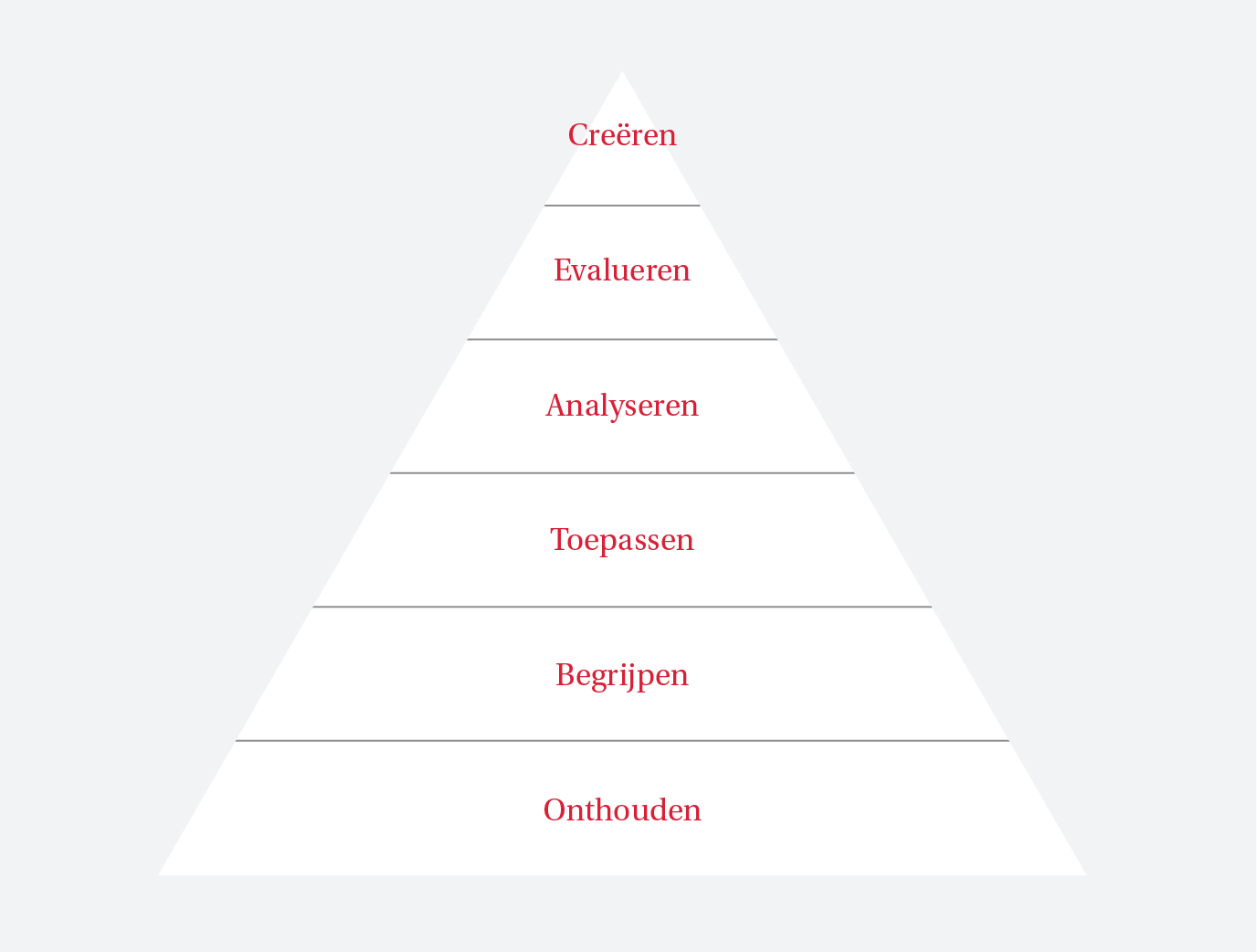
Bloom’s Taxnonmy (Create/Evaluate/Analyse/Apply/Understand/Remember)
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom distinguishes between six levels of thinking. The first two levels, remembering and understanding,tend to stimulate superficial learning. Students take in information and are capable of reproducing this information. A drawback of this type of learning is that new information is easily forgotten again. For this reason, a deeper learning should be aimed for in higher education. This allows students to apply, analyse and evaluate information, and create new information or knowledge. These skills are usually thought of as higher-order thinking skills,and it is expected that information is more easily retained if these skills are invoked. In Bloom’s revised taxonomy, the level of synthesis has been added. This refers to students’ ability to combine information from different sources. The video below outlines Bloom’s taxonomy and explains ho wit may be used in the development of assignments.